AWS Lambda Getting Started¶
In this tutorial we will look at getting an AWS Lambda function running in AWS and exercise it with a node.js tool.
NOTE: You'll need a working AWS account for this tutorial.
Create the Lambda Function¶
A Lambda function is essentially a snippet of code that is run because of some condition that we configure. It is not associated with a particular server. Instead, as we'll see, we select a runtime environment that is provided on some compute capacity that AWS has that can run the snippet when the conditions are correct.
Conditions could be a queue entering a message queue, or a certain time is reached (a bit like cron), etc.
Sign into AWS and select the Lambda server (Using the Find Services search function)
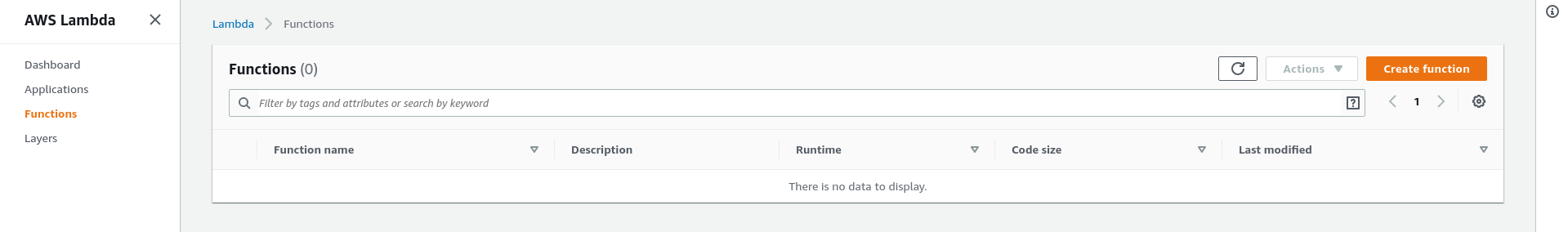
Click Create Function
Select Author from scratch if it isn't already selected and fill in the Function name with something that makes sense, something like awsLambdaTutorial.
Leave the runtime set to the latest Node.js (It's 12.x as of writing this tutorial)
There's no need to do anything much with the execution role. If you expand the options you'll see that the default action is to create a new role with basic Lambda permissions. This is ideal as we don't want the Lambda to have permissions to do anything inside our account right now.
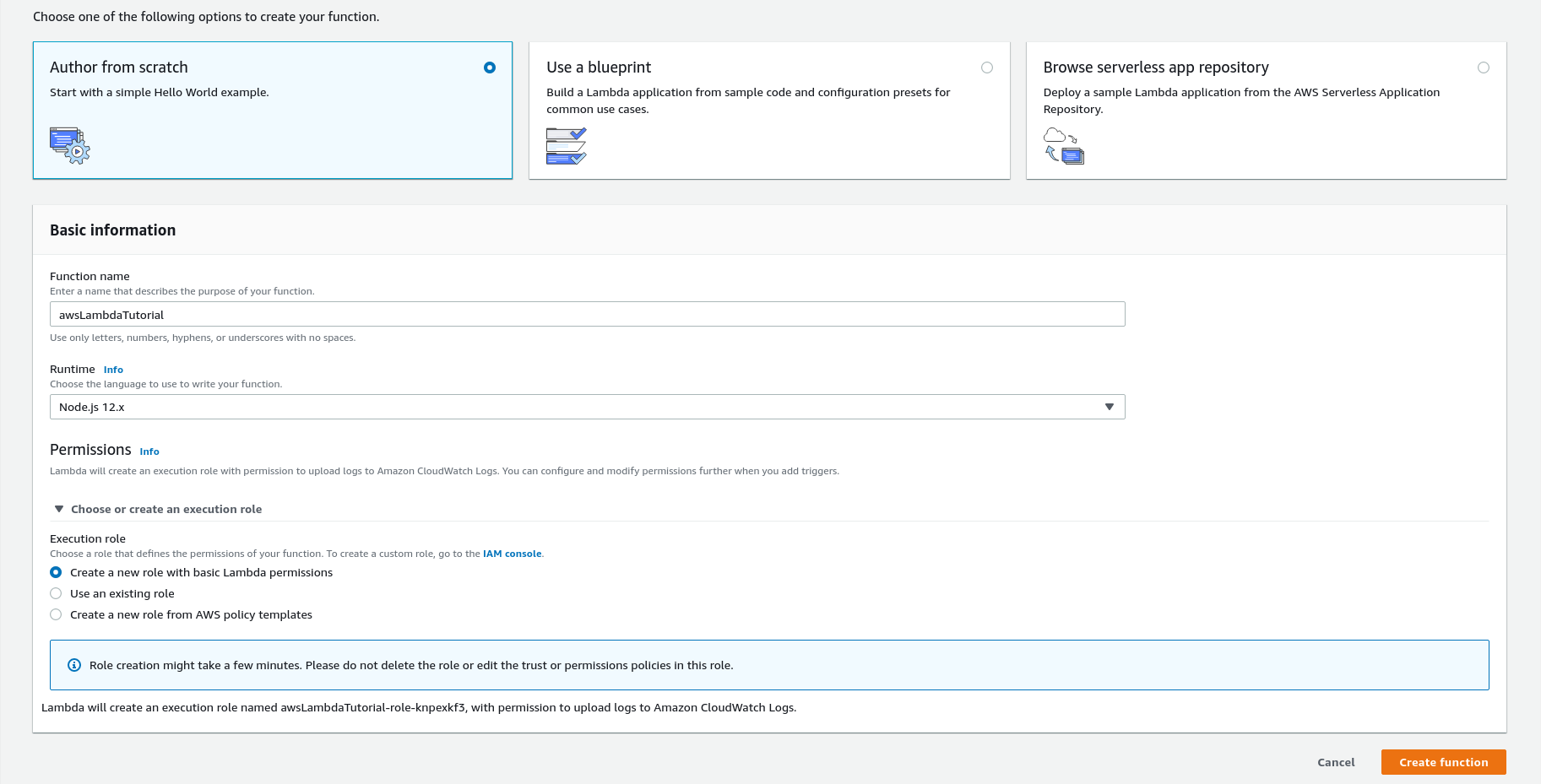
Click Create Function to now go ahead and create the Lambda function.
Don't be put off by the next screen, there's quite a lot on there. What we have now is an index.js that is filled with an example Lambda function:
exports.handler = async (event) => {
// TODO implement
const response = {
statusCode: 200,
body: JSON.stringify('Hello from Lambda!'),
};
return response;
};
This shows a basic HTTP handler that will return a HTTP status code of 200 OK along with a JSON formatted body that reads Hello from Lambda!.
Not particularly exciting stuff, but a Hello World! example rarely is. Getting this working is an achievement however.
There's nothing left for us to do here - we've created the Lambda function. So now what!?
We need to trigger the Lambda function. Although it exists, there's currently no way of invoking the Lambda.
Create an API Gateway¶
We can go ahead and create an API Gateway and attach an API endpoint to the Lambda in order to trigger it.
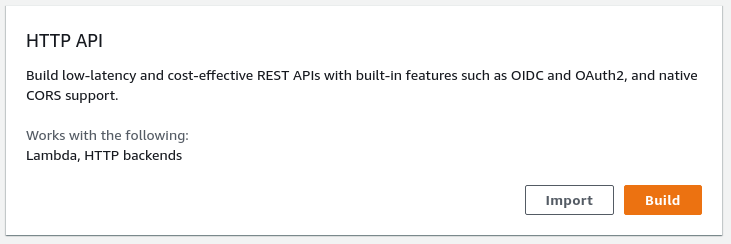
Switch to the API Gateway Service in the AWS Console and select HTTP API by clicking Build on the HTTP API dialog:
Click Add Integration and select Lambda from the dropdown list to start integrating the API to the Lambda function.
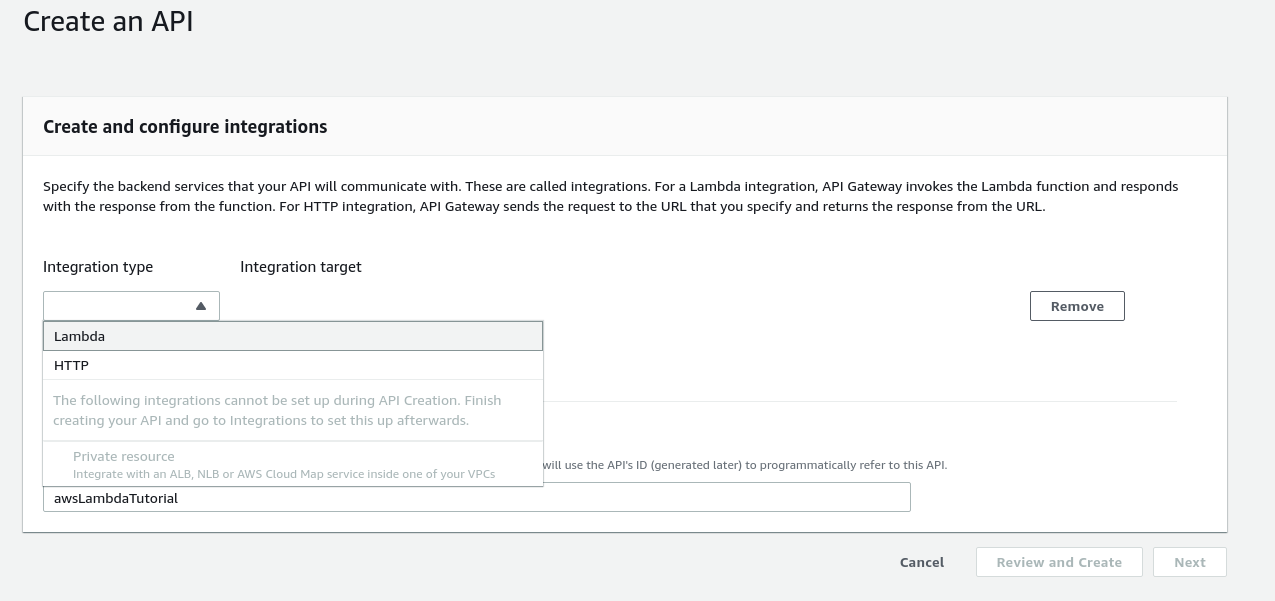
Leave the Integration Target as the default - it should match the Lambda Function you created at the start. Select the awsLambdaTutorial Lambda as the target.
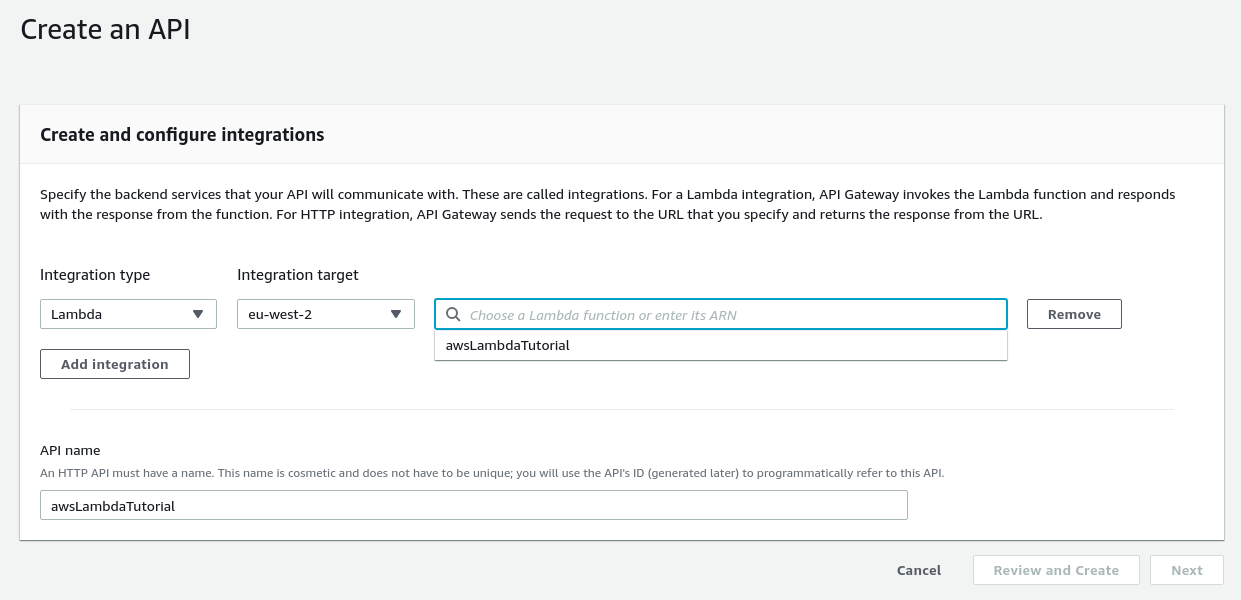
Give the API a name like awsLambdaTutorial and click Next:
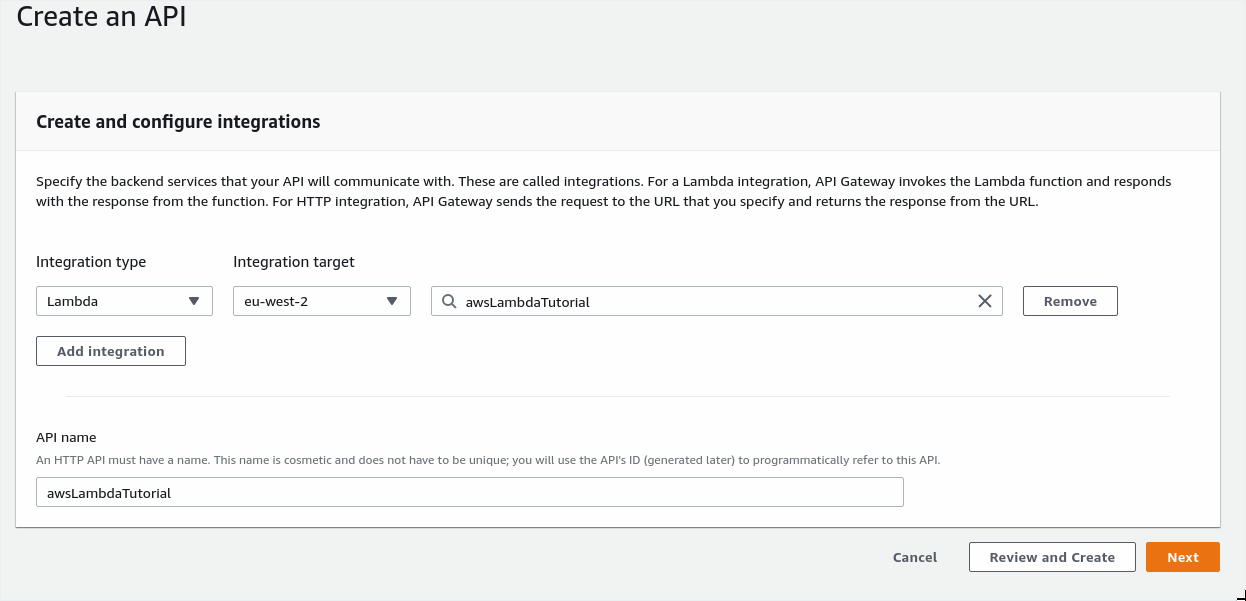
On the next page we can see that the roue /awsLambdaTutorial in the HTTP API will result in use running the target lambda. The Method by default is set to ANY. Might as well leave all of this as default - although we'll only be using the GET for the turorial.
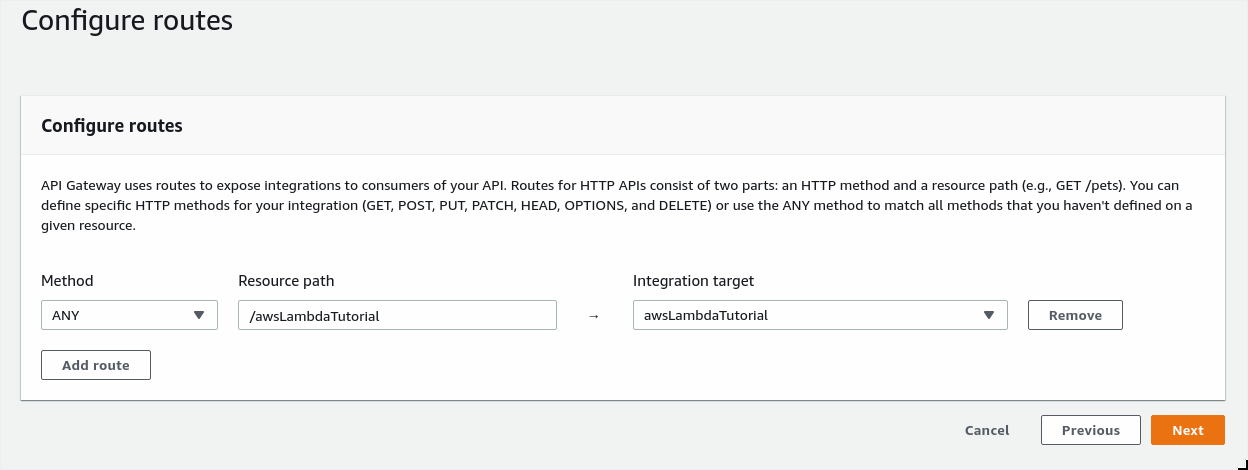
The Stages section can just be left as $default - we won't be doing any fancy API versioning for this tutorial. Click Next.
In the review page, click Create to create the API Gateway.
The next page gives us information about the API Gateway - it's live already and had a unique API Gateway URL which can be used straight away.
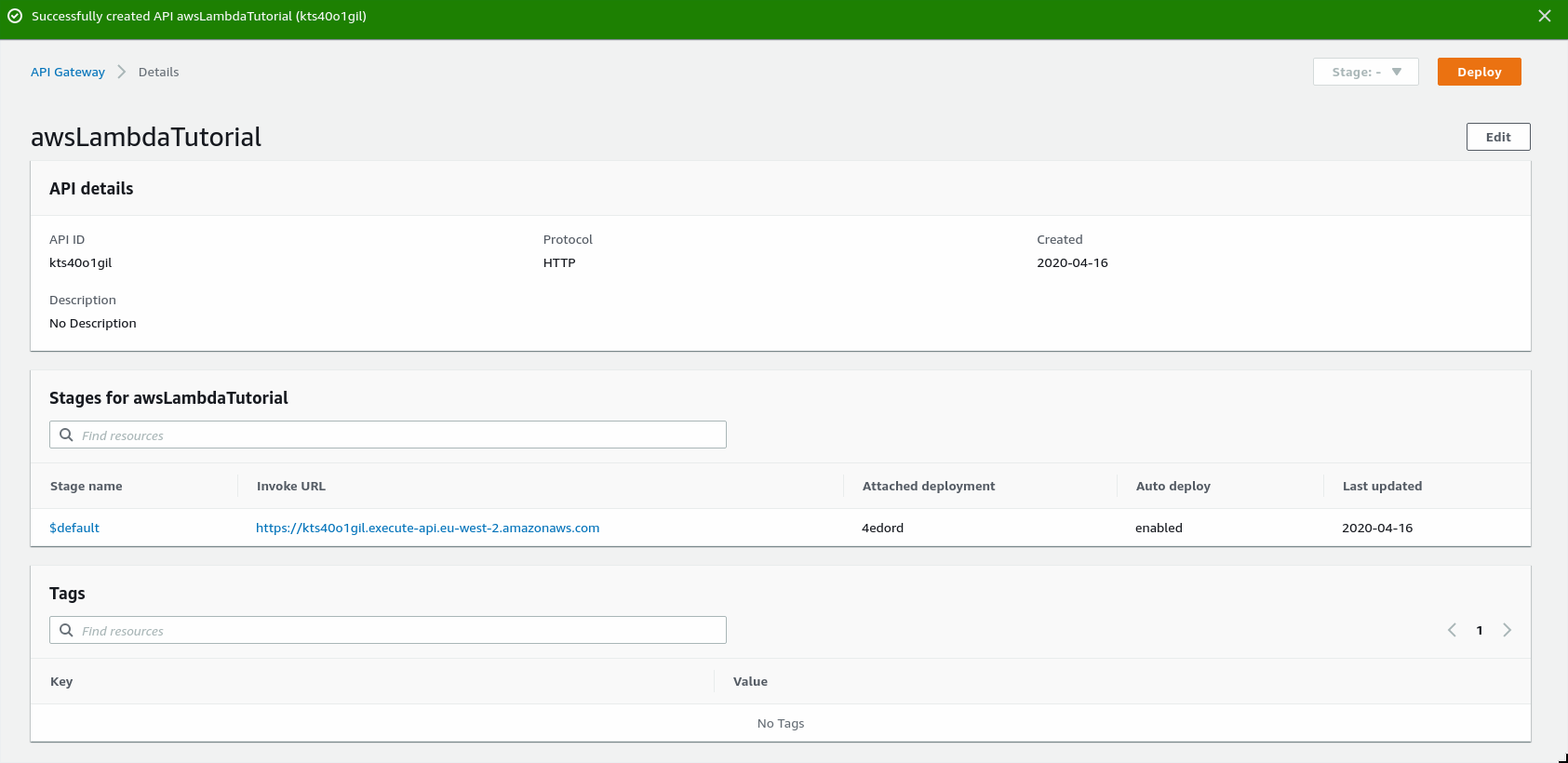
Using the route from earlier in the process and the API URL shown after creation we can exercise the Lambda function using a HTTP call to the API e endpoint we connected to the Lambda:
$ curl -v https://kts40o1gil.execute-api.eu-west-2.amazonaws.com/awsLambdaTutorial
* Trying 3.10.172.190:443...
* TCP_NODELAY set
* Connected to kts40o1gil.execute-api.eu-west-2.amazonaws.com (3.10.172.190) port 443 (#0)
* ALPN, offering h2
* ALPN, offering http/1.1
* successfully set certificate verify locations:
* CAfile: /etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crt
CApath: none
* TLSv1.3 (OUT), TLS handshake, Client hello (1):
* TLSv1.3 (IN), TLS handshake, Server hello (2):
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Certificate (11):
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Server key exchange (12):
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Server finished (14):
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, Client key exchange (16):
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS change cipher, Change cipher spec (1):
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, Finished (20):
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Finished (20):
* SSL connection using TLSv1.2 / ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256
* ALPN, server accepted to use h2
* Server certificate:
* subject: CN=*.execute-api.eu-west-2.amazonaws.com
* start date: Jan 27 00:00:00 2020 GMT
* expire date: Feb 27 12:00:00 2021 GMT
* subjectAltName: host "kts40o1gil.execute-api.eu-west-2.amazonaws.com" matched cert's "*.execute-api.eu-west-2.amazonaws.com"
* issuer: C=US; O=Amazon; OU=Server CA 1B; CN=Amazon
* SSL certificate verify ok.
* Using HTTP2, server supports multi-use
* Connection state changed (HTTP/2 confirmed)
* Copying HTTP/2 data in stream buffer to connection buffer after upgrade: len=0
* Using Stream ID: 1 (easy handle 0x557e0ea27200)
> GET /awsLambdaTutorial HTTP/2
> Host: kts40o1gil.execute-api.eu-west-2.amazonaws.com
> User-Agent: curl/7.66.0
> Accept: */*
>
* Connection state changed (MAX_CONCURRENT_STREAMS == 128)!
< HTTP/2 200
< date: Thu, 16 Apr 2020 21:16:28 GMT
< content-type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
< content-length: 20
< apigw-requestid: LGSu_i1cLPEEPNw=
<
* Connection #0 to host kts40o1gil.execute-api.eu-west-2.amazonaws.com left intact
"Hello from Lambda!"
We have successfully run the Lambda function with an incoming HTTP request. This is a good starting point for getting further into Lambda functions.